Flexbox Attributes
Litho uses the Yoga library, which is an implementation of Flexbox, to measure and layout on-screen components. Users familiar with Flexbox on the web should have no problems. For users familiar with how Android normally performs Layout, Flexbox will remind them of LinearLayout.
This page shows how various attributes of Flexbox are used for on-screen layout.
Layout direction
Flexbox is a one-dimensional layout model, which means all elements are placed along one line.
The following information may help assist in deciding whether to layout elements horizontally or vertically.
The primary axis of layout is called the Main Axis, and the direction perpendicular to it is called the Cross Axis. For example, if children are to be laid out left to right, then the Main Axis would be the horizontal axis, and the Cross Axis would be the vertical axis.
Litho uses special container components to define the direction of the layout, as shown in the following table.
| Component | Main Axis | Child Elements Layout | If Wrapping is Enabled |
|---|---|---|---|
Row | horizontal | left to right | Next line will start under the first item on the left of the container. |
Row (reverse) | horizontal | right to left | Next line will start under the first item on the right of the container. |
Column | vertical | top to bottom | Next line will start to the right of the first item on the top of the container. |
Column (reverse) | vertical | bottom to top | Next line will start to the right of the first item on the bottom of the container. |
The above container components are illustrated in the following diagram.
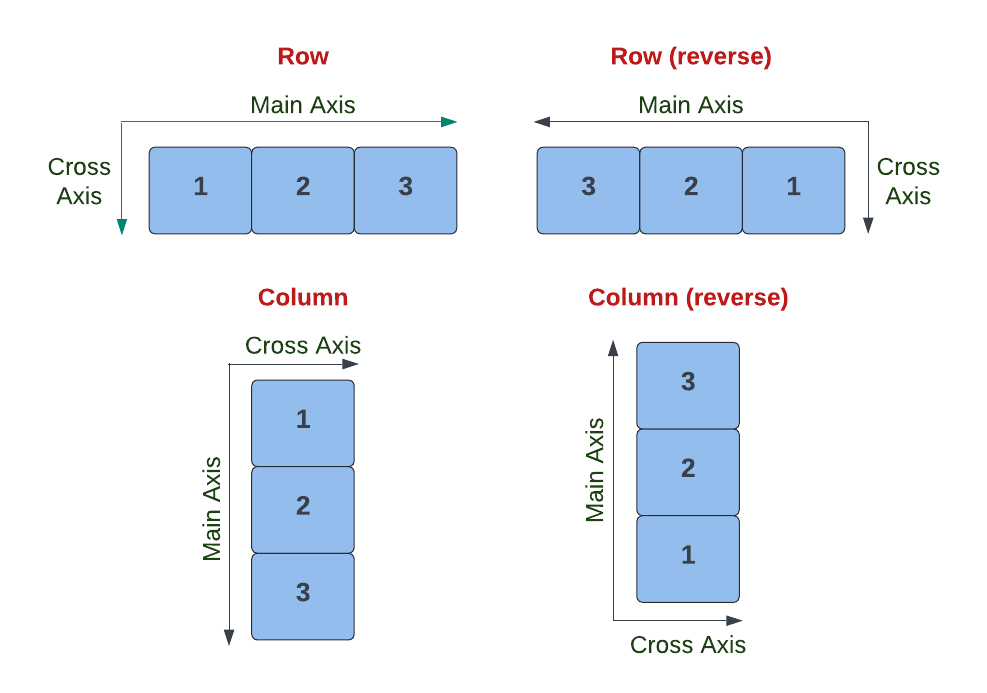
The (reverse) option is available through the .reverse(boolean) method on Row/Column objects.
Distribution along the main axis
If your container has more space than is necessary along the Main Axis then the way children are positioned across that axis needs to be considered.
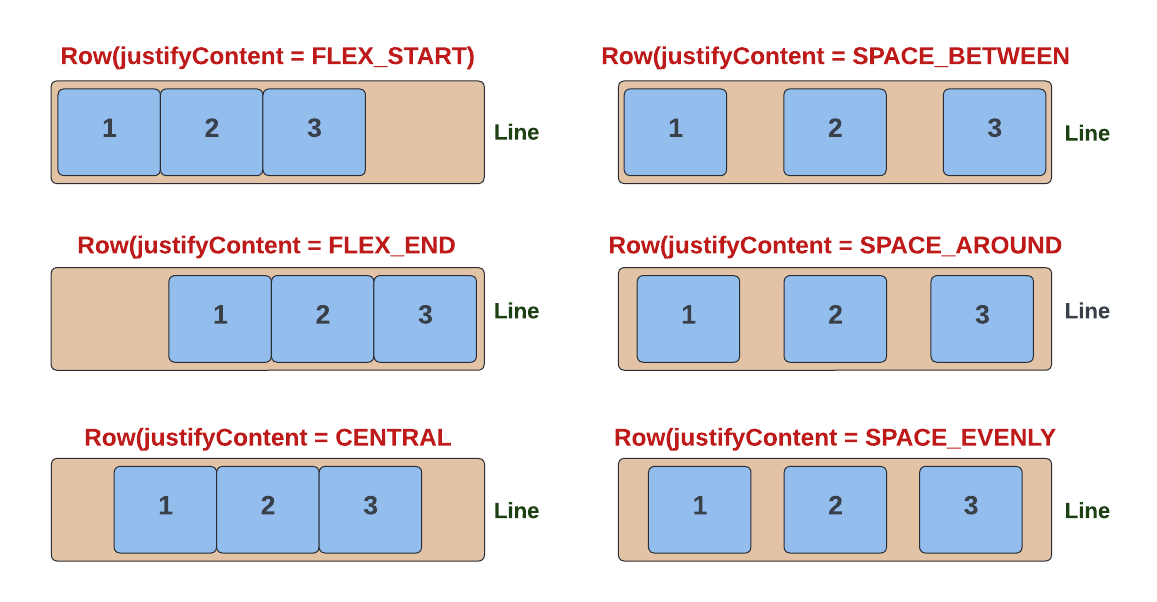
The justifyContent method specifies how the child elements are distributed across the Main Axis. It takes a YogaJustify enum input, which has the following possible values:
FLEX_START(default) - position children at the start of the container, along the main axis.FLEX_END- position children at the end of the container, along the main axis.CENTER- position children in the centre of the container, along the main axis.SPACE_BETWEEN- distribute extra space evenly between children.SPACE_AROUND- distribute space evenly around each child. Note that adjacent children will have '2x' space between them (because each child has its own 'padding').SPACE_EVENLY- distribute space evenly around all children.
The YogaJustify values are illustrated below.
Distribution along the cross axis
If the elements in your line have different heights, then the way they are positioned along the line needs to be considered.
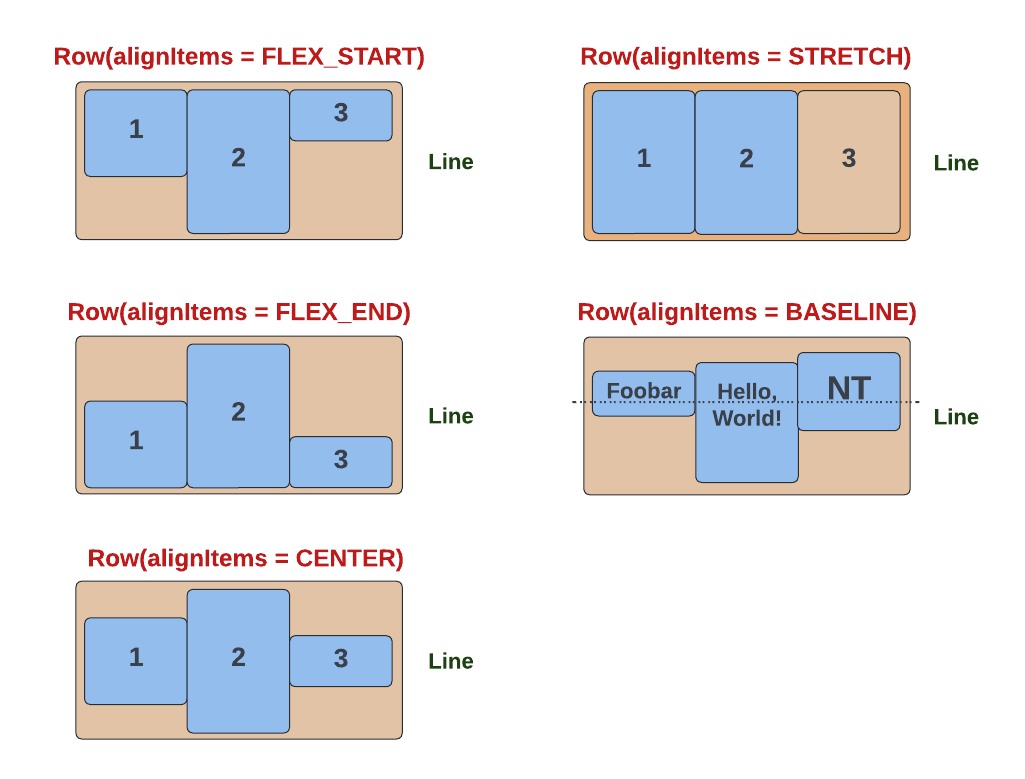
The alignItems method specifies how the container's children are distributed across the Cross Axis. It takes a YogaAlign enum input, which has the following possible values:
STRETCH(default) - stretch the size of all elements to completely fill the line.FLEX_START- align elements with the start of the cross axis.FLEX_END- align elements with the end of the cross axis.CENTER- align elements with the centre of the line.BASELINE- align elements with respect to their baselines.
The YogaAlign values are illustrated below.
Wrapping to multiple lines
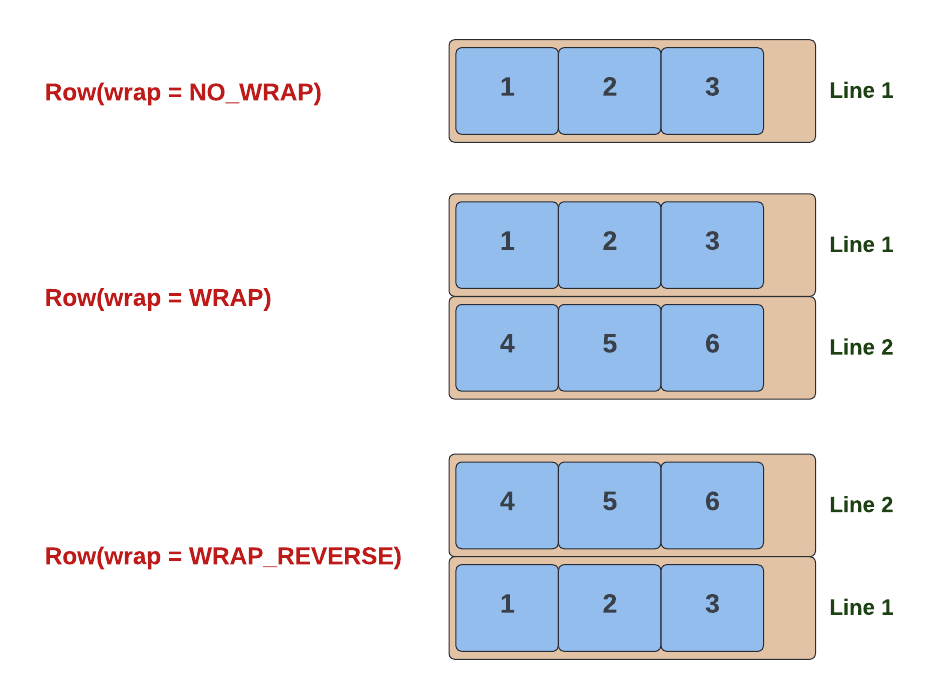
In addition to the one-dimensional Flexbox laying out its children in one line, Flexboxes can also wrap their children onto multiple lines, much like text wraps. Wrapping behavior is specified with the Wrap method, which takes a YogaWrap enum value that has the following possible values:
NO_WRAP(default) - there is no wrapping. Children are forced into a single line; if they cannot fit, they will overflow.WRAP- elements that overflow a single line will be moved to the next line. If the main axis is horizontal, then the next line will be below the previous line.WRAP_REVERSE- similar toWRAPexcept the order of lines is reversed. If the main axis is horizontal, then the next line will be above the previous line.
The YogaWrap values are illustrated below.
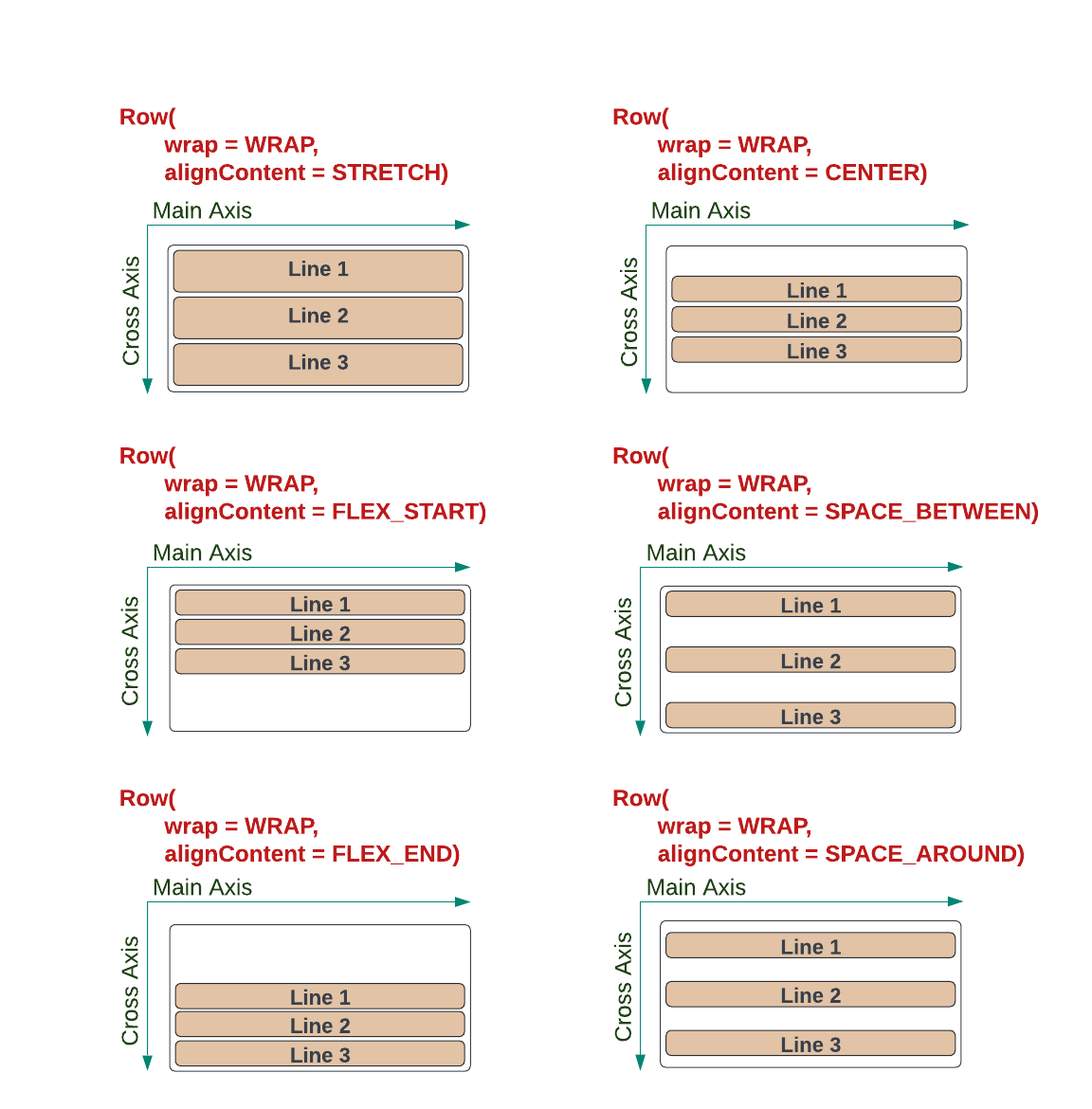
Line distribution
If the container has extra space in the Cross Axis direction, then the way lines are distributed in that space needs to be considered.
The alignContent method specifies how lines are distributed along the Cross Axis. It takes a YogaAlign enum value, which has the following possible values:
STRETCH(default) - lines are stretched evenly to fill the available space in the cross axis.FLEX_START- lines are placed at the start of the cross axis.FLEX_END- lines are placed at the end of the cross axis.CENTER- lines are placed in the centre of the cross axis.SPACE_BETWEEN- evenly distributes extra space between all lines.SPACE_AROUND- pads lines above and below with extra space.
The YogaAlign values, for Lines, are illustrated below.
For more information on specific Flexbox properties, refer to the Yoga documentation or explore any web resource on how Flexbox functions.